1. Heparan sulfate in brain health and disease.
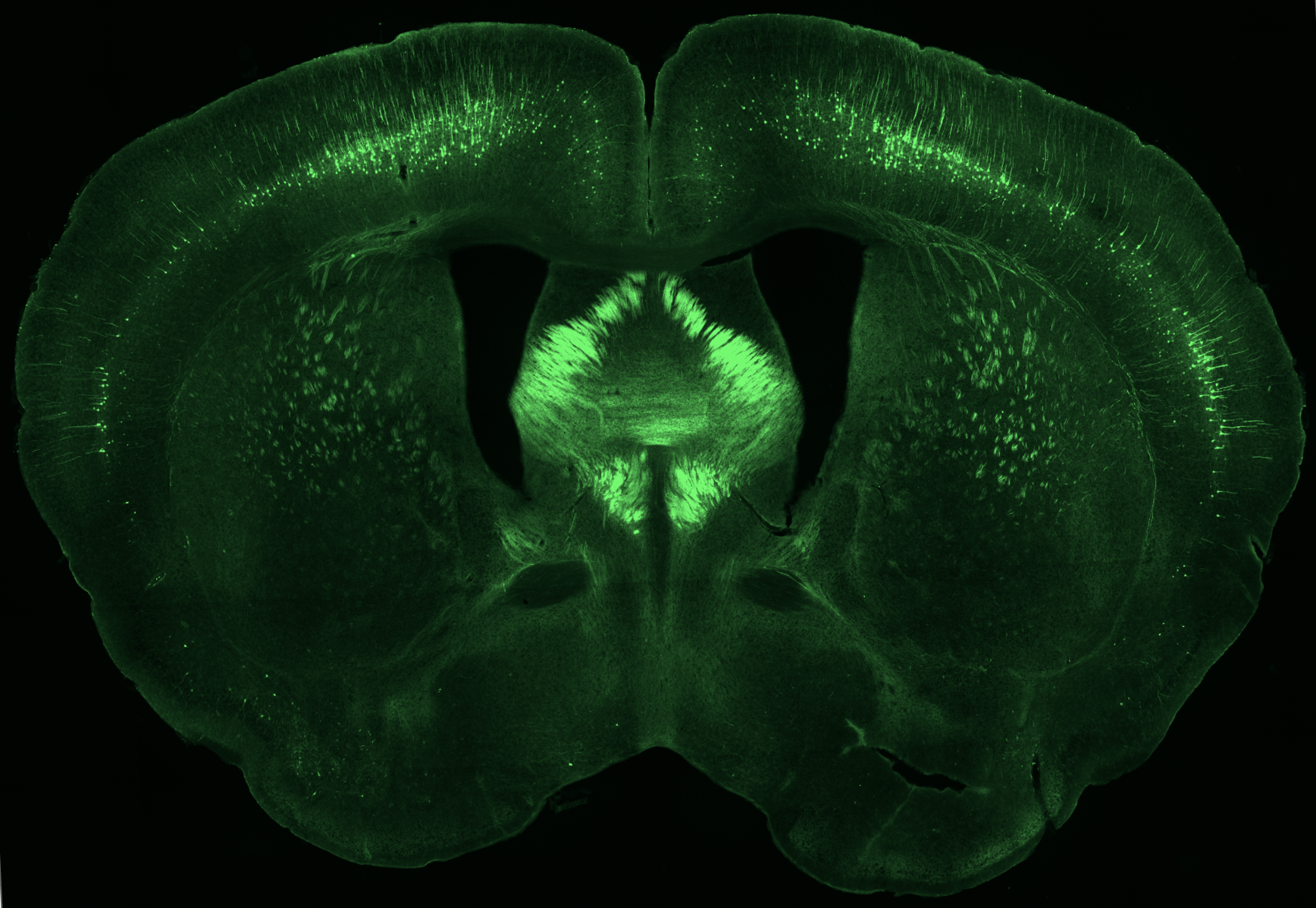
Heparan sulfate (HS) is a sugar molecule that covers the surface of all human cells, including the more than 200 billion cells in the brain. However, the role and mechanisms of HS in the brain remain largely unknown. HS is also associated with a series of brain disorders, such as Alzheimer’s disease, Parkinson’s disease, intellectual disability, and Kallmann syndrome. How HS contributes to these brain disorders remains poorly understood, and current therapies are limited. Our long-term goal is to reveal how HS regulates brain function and contributes to brain disorders, with the hope to eventually develop a cure. We are currently focused on HS enzymes, particularly the three 6-O-sulfotransferases (HS6ST1-3) and the two sulfatases (SULF1,2).
Fundings:
The NIH National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke (NINDS)
The Alzheimer’s Association
The Mizutani Foundation for Glycoscience (Japan)
The Adele Smithers Parkinson’s Disease Center
Publications:
1). Sohyun Moon, Ying-Tao Zhao, Glycobiology, 2021
2). Sohyun Moon, Ying-Tao Zhao, Human Molecular Genetics, 2022
3). Sohyun Moon, … Jerry Yingtao Zhao, Glycobiology, 2024
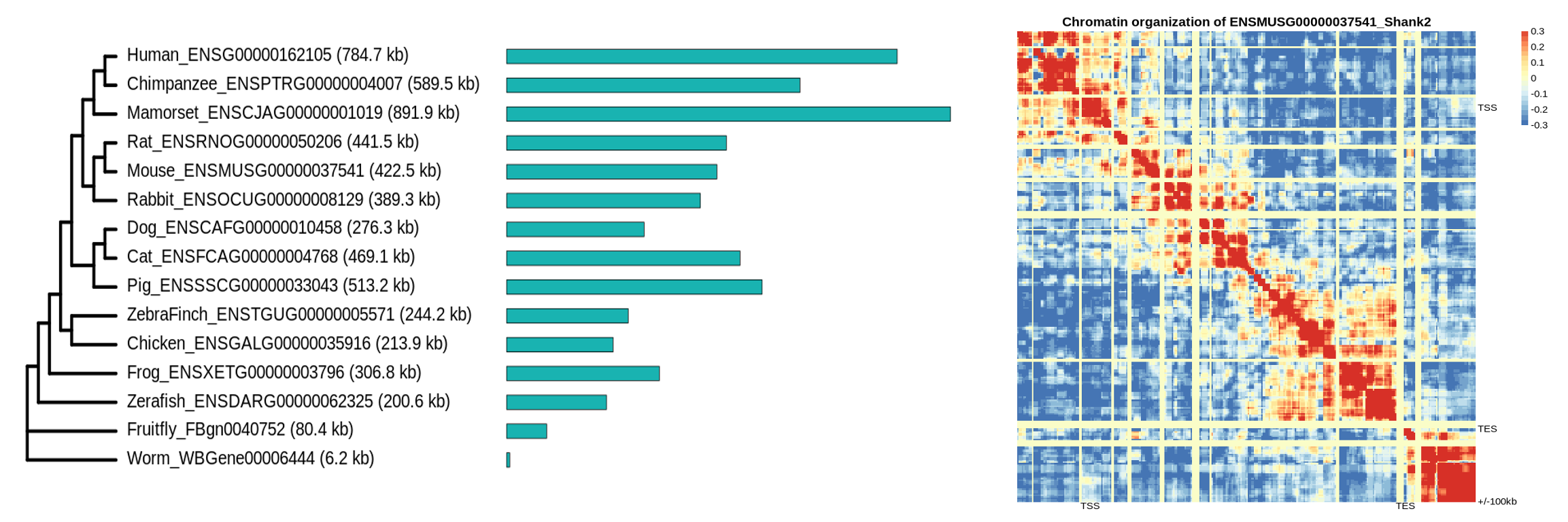
2. Long genes in brain health, disease, and evolution.
Genes in the human genome have different lengths, which can vary by more than 10,000-fold. The regulation of short genes is well studied, but the regulation of long genes remains largely unknown. This represents a critical need because long genes are preferentially expressed in the brain and are dysregulated in multiple brain disorders such as autism and Alzheimer’s disease. Due to its length, a long gene needs more energy and time to be transcribed, which exhibits a clear disadvantage compared to a short gene. Intriguingly, despite this disadvantage, hundreds of genes become longer and longer during evolution, but why and how this is happening remains largely unknown. Our long-term goal is to use genomics, epigenetics, and mouse models to identify the regulation mechanisms of long genes in the brain and to reveal the etiology of long gene-associated brain disorders. We are particularly interested in the chromatin organization, transcription, splicing, and evolution of long genes.
Fundings:
None
Publications:
1). Ying-Tao Zhao, … Zhaolan Zhou, Genome research, 2018
2). Brian Johnson, Ying-Tao Zhao, Maria Fasolino, … Zhaolan Zhou, Nature Medicine, 2017
3). Sohyun Moon, Ying-Tao Zhao, PLOS ONE, 2022
4). Yura Kim, Mariam Naghavi, Ying-Tao Zhao, bioRxiv, 2020